In the boy’s fourth month, researchers were meeting with the Food and Drug Administration to discuss regulatory approval for a clinical trial—a trial where KJ would be the only participant. They were also working with the institutional review board (IRB) at Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia to go over the clinical protocol, safety, and ethical aspects of the treatment. The researchers described the unprecedented speed of the oversight steps as being “through alternative procedures.”
In month five, they started toxicology testing in mice. In the mice, the experimental therapy corrected KJ’s mutation, replacing the errant A-T base pair with the correct G-C pair in the animals’ cells. The first dose provided a 42 percent whole-liver corrective rate in the animals. At the start of KJ’s sixth month, the researchers had results from safety testing in monkeys: Their customized base-editing therapy, delivered as mRNA via a lipid nanoparticle, did not produce any toxic effects in the monkeys.
A clinical-grade batch of the treatment was readied. In month seven, further testing of the treatment found acceptably low-levels of off-target genetic changes. The researchers submitted the FDA paperwork for approval of an “investigational new drug,” or IND, for KJ. The FDA approved it in a week. The researchers then started KJ on an immune-suppressing treatment to make sure his immune system wouldn’t react to the gene-editing therapy. Then, when KJ was still just 6 months old, he got a first low dose of his custom gene-editing therapy.
“Transformational”
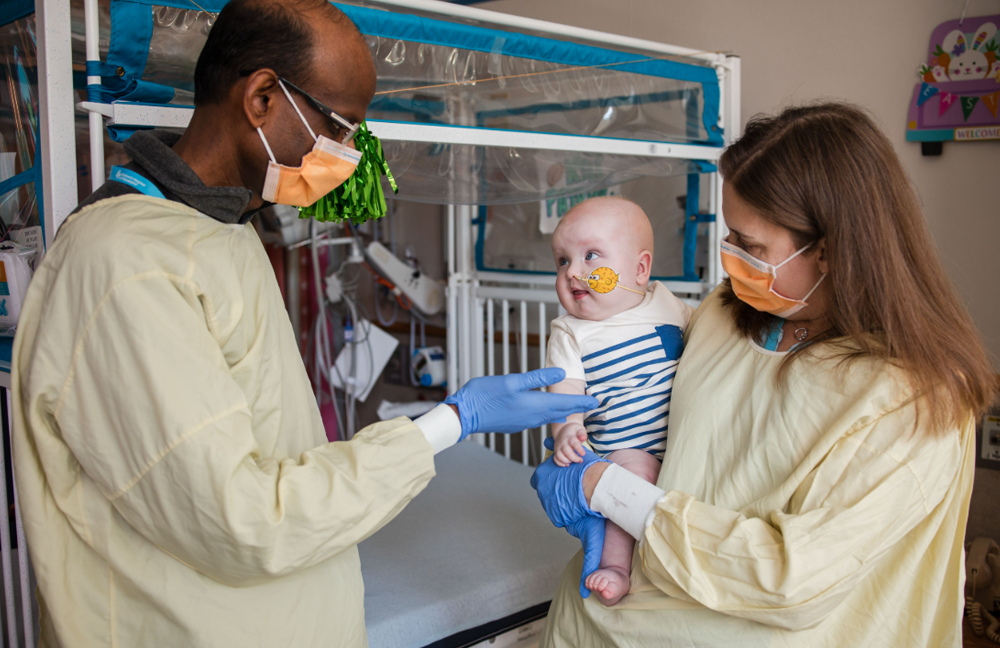
After the treatment, he was able to start eating more protein, which would have otherwise caused his ammonia levels to skyrocket. But he couldn’t be weaned off of the drug treatment used to keep his ammonia levels down (nitrogen scavenging medication). With no safety concerns seen after the first dose, KJ has since gotten two more doses of the gene therapy and is now on reduced nitrogen scavenging medication. With more protein in his diet, he has moved from the 9th percentile in weight to 35th or 40th percentile. He’s now about 9 and a half months old, and his doctors are preparing to allow him to go home from the hospital for the first time. Though he will have to be closely monitored and may still at some point need a liver transplant, his family and doctors are celebrating the improvements so far.